Planter boxes are becoming an increasingly popular feature in modern construction, adding aesthetic value and greenery to residential and commercial projects. However, constructing a planter box involves more than simply building a container for soil and plants. These structures are water-retaining and often difficult to maintain, which means careful planning and execution are essential to prevent issues during the warranty period and throughout the life of the building.
Why care is needed
Planter boxes function in a similar way to swimming pools that are attached to a building. They hold water and are not easily accessible for routine maintenance. Any failure in construction or waterproofing can result in water leakage, which can damage the structure, finishes, and surrounding areas. For this reason, precise workmanship and proactive risk management are critical to ensure the long-term performance of planter boxes.
Managing the risks
1. Drainage
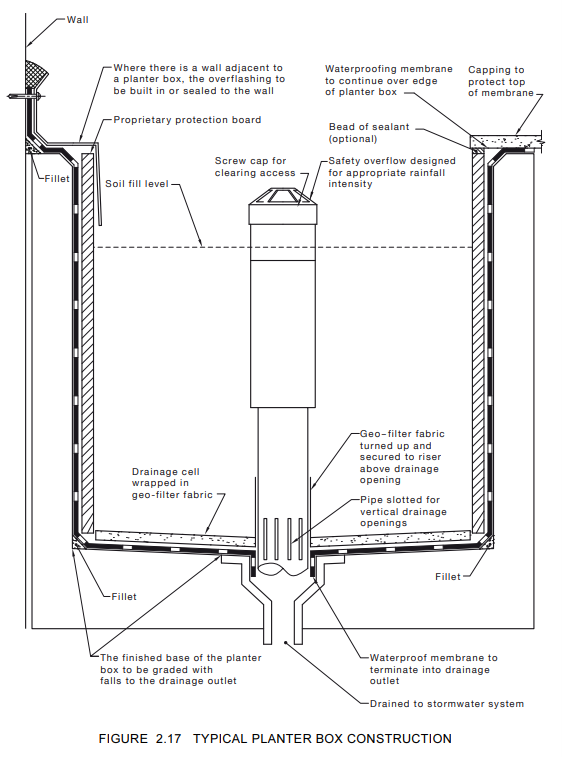
Adequate drainage is one of the most important aspects of planter box construction. Excess water must be removed effectively to prevent pooling and reduce stress on the waterproofing system. This is typically achieved using a slotted standpipe connected to the waste outlet. The number and size of drains should be carefully calculated by the designer based on the size and depth of the planter. In addition, connecting an agricultural drain to the standpipe as a “T” connection can provide extra protection against overflow. Proper drainage ensures water is efficiently directed away from the planter, minimising the risk of leaks or water damage.
2. Falls
The base of the planter should be graded, or “fall,” toward the waste outlet. Correct falls ensure that water does not pool at the bottom, which could compromise the waterproofing membrane over time. Ensuring proper falls is a simple but crucial step that significantly contributes to the longevity of the structure.
3. Membrane
Selecting the correct waterproofing membrane is essential. A qualified waterproofing contractor should specify the appropriate product and installation method. Using the right membrane, applied correctly, protects both the builder and the subcontractor and ensures the planter is fully waterproofed.
4. Maintenance
Regular maintenance is required to keep plant roots, leaves, and garden debris from damaging the membrane. This includes pruning, clearing debris, and monitoring the soil and plant health to prevent excessive moisture build-up.
5. Handover documents
Comprehensive handover documentation is essential. Provide the property owner with all relevant information about the planter box, including maintenance requirements. Clear documentation helps set expectations and ensures the owner understands their responsibility in maintaining the planter, which prolongs the lifespan of the structure.
6. Irrigation
If the planter includes an irrigation system, care must be taken to avoid penetrating the planter or damaging the membrane during installation. Properly installed irrigation systems should complement the drainage system and avoid compromising the waterproofing.
By carefully addressing drainage, falls, membrane selection, maintenance, handover documentation, and irrigation, builders and subcontractors can significantly reduce the risk of defects, protect the structure, and ensure the long-term performance of planter boxes. Proper planning and execution not only safeguard the building but also enhance the overall quality and longevity of the project.
Detail Below: Typical Planter Box Construction
Reference: Waterproofing for external above-ground use- AS4654.2-2012





